利用 HomeAssistant +树莓派+ Amazon Echo 的智能家居实践(二)—— 初识 HomeAssistant
这一篇我们要开始学习使用 HomeAssistant 了。在此之前,为了更方便地写代码,我们还需要做一些准备工作。
(一)开启 Samba
还记得上一节中我们使用的 FTP 软件吗?你可以在 /home/pi/hassbian-scripts 这个目录下找到一些已经预装好的脚本,如果没有,可以以 pi 的身份 clone 这个 repo :
git clone https://github.com/home-assistant/hassbian-scripts.git
然后运行
sudo ./hassbian-scripts/install_samba.sh
大概5分钟左右的安装时间。安装完你可以看到下面的界面:
然后在 Finder 的共享下面看到树莓派开放的服务器了。这样的好处是,你可以像访问本地的文件一样访问树莓派上的文件了。
然后就可以用 Sublime Text 打开这个目录开始编辑了:
(二)Configuration.yaml
集成的所有服务可以在 Components 页面搜索。

接下去我们的所有工作都是在 Configuration.yaml 这个文件里完成。 HomeAssistant 的配置文件是 Yaml 写的,每个字段都表示一个服务,比如 homeassistant: ,introduction,http,sun,sensor .... 等都是 HomeAssistant 内建好的服务。一般来说,你需要什么服务就添加什么服务,重启 HA 即可在控制页面看到新添加的服务了。
凡是改动了 Configuration.yaml 配置文件,都需要重启 HomeAssistant 服务才能生效。你可以使用命令重启,
sudo systemctl restart home-assistant.service
也可以在管理界面重启
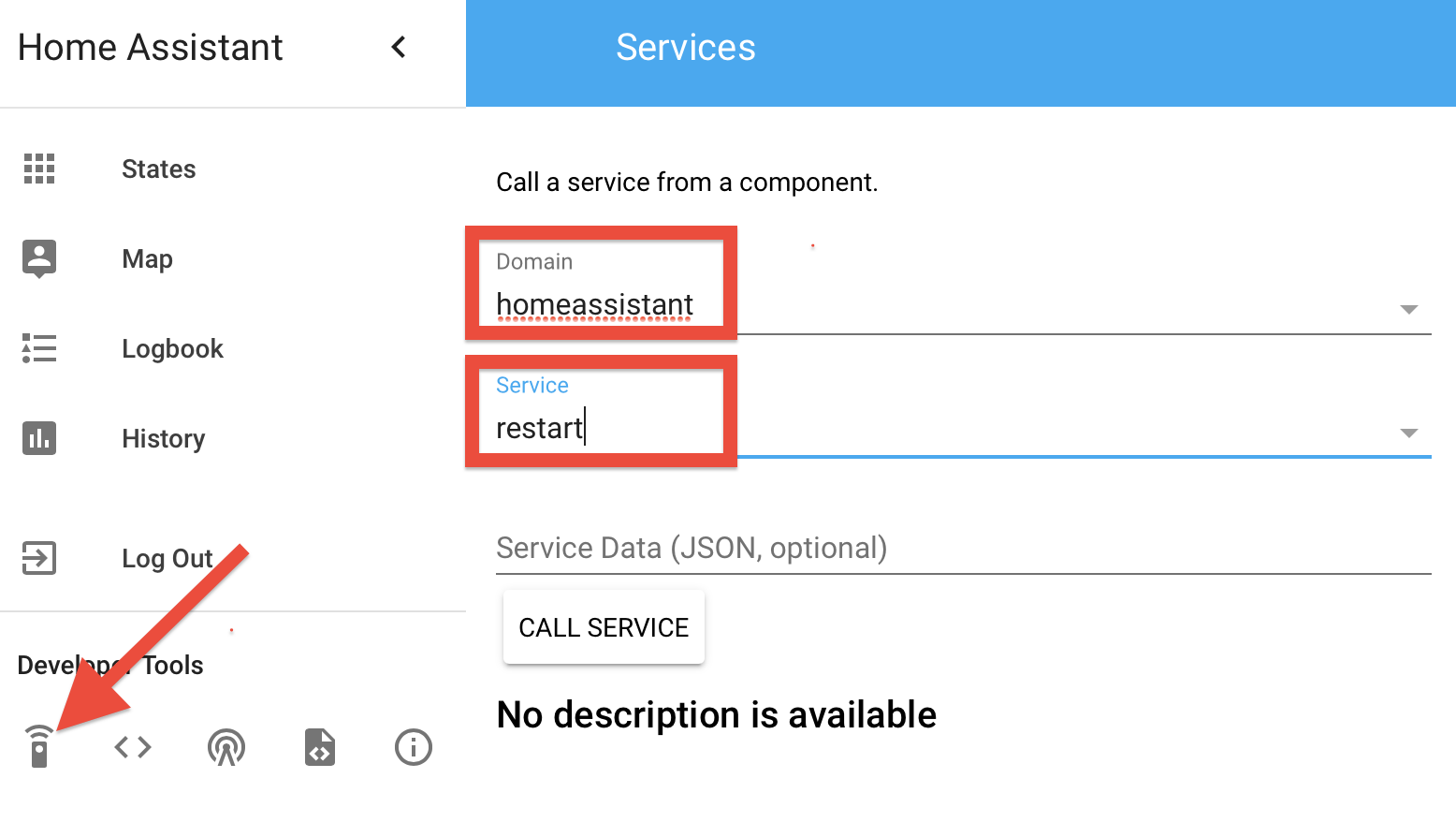
举些例子:
1. homeassistant 文档
这个服务下面提供一些全局的信息配置。latitude 和 longitude 字段填入自己所在位置的经纬度,方便一些需要用到经纬度的服务准确获取信息,比如 sunrise 服务就可以准确获取你当前位置的日出日落时间;unit_system 使用英制单位还是公制单位;time_zone 你的时区....
2. automation 文档
这是一个内置的自动机,类似 IFTTT,都是当满足条件时触发操作,但 automation 的操作空间比 IFTTT 大的多,他不仅可以设置多个条件,还有触发一系列操作。
automation 由三部分组成:
trigger -- When Paulus arrives home
condition -- and it is after sunset:
action -- Turn the lights in the living room on
举个我使用的例子:
- HomeAssistant 服务启动时候用 IFTTT 给我推送一条推送:
automation 1:
alias: 'Startup Notification'
trigger:
- platform: event
event_type: homeassistant_start
action:
- service: ifttt.trigger
data: {"event":"homeassistant_start", "value1":"Home Assistant 已启动"}
其中 trigger 的 platform 字段必须制定一个值, event(事件总线) 是 HA 内建的一个 platform ,任何服务都可以获取和监听系统事件总线的事件,比如 HOMEASSISTANT_START , HOMEASSISTANT_STOP , SERVICE_REGISTERED .... 我在上面的 automation 里监听了 HA 启动的事件,没有 condition ,直接触发 action,action 的 service 也必须指定一个服务。
3. notify 文档
这就是 HA 的推送服务了,基本你能想到的和你想不到的 platform 都已经集成进来了,具体请看文档。比如我用的是 pushbullet。
notify:
- name: notify
platform: pushbullet
api_key: xxxxx
一旦配置了这个服务,就可以在其他服务里调用它了。比如在我们之前提到的 automation 里面就可以使用:
automation 3:
- alias: Send message at lunch time
trigger:
platform: time
hours: 12
minutes: 15
seconds: 0
action:
service: notify.notify
data:
message: '该吃午饭了'
title: '为了健康,请规律饮食!'
注意我这里的 action 就用了 notify.notify 来找到你在其他地方配置的这个 notify 服务。
4. IFTTT 文档
ifttt:
key: xxxxx-x-xxxxxxxxxxxxx
IFTTT 的配置很简单,就只要配一个 key 就行,key 需要在 Maker Channel 里生成。接下来我们来看看如果配合 IFTTT 使用 HomeAssistant。
首先新建一个 Applet, this 选择 Maker Webhooks,选择 Receive a web request,然后给事件取一个名字。
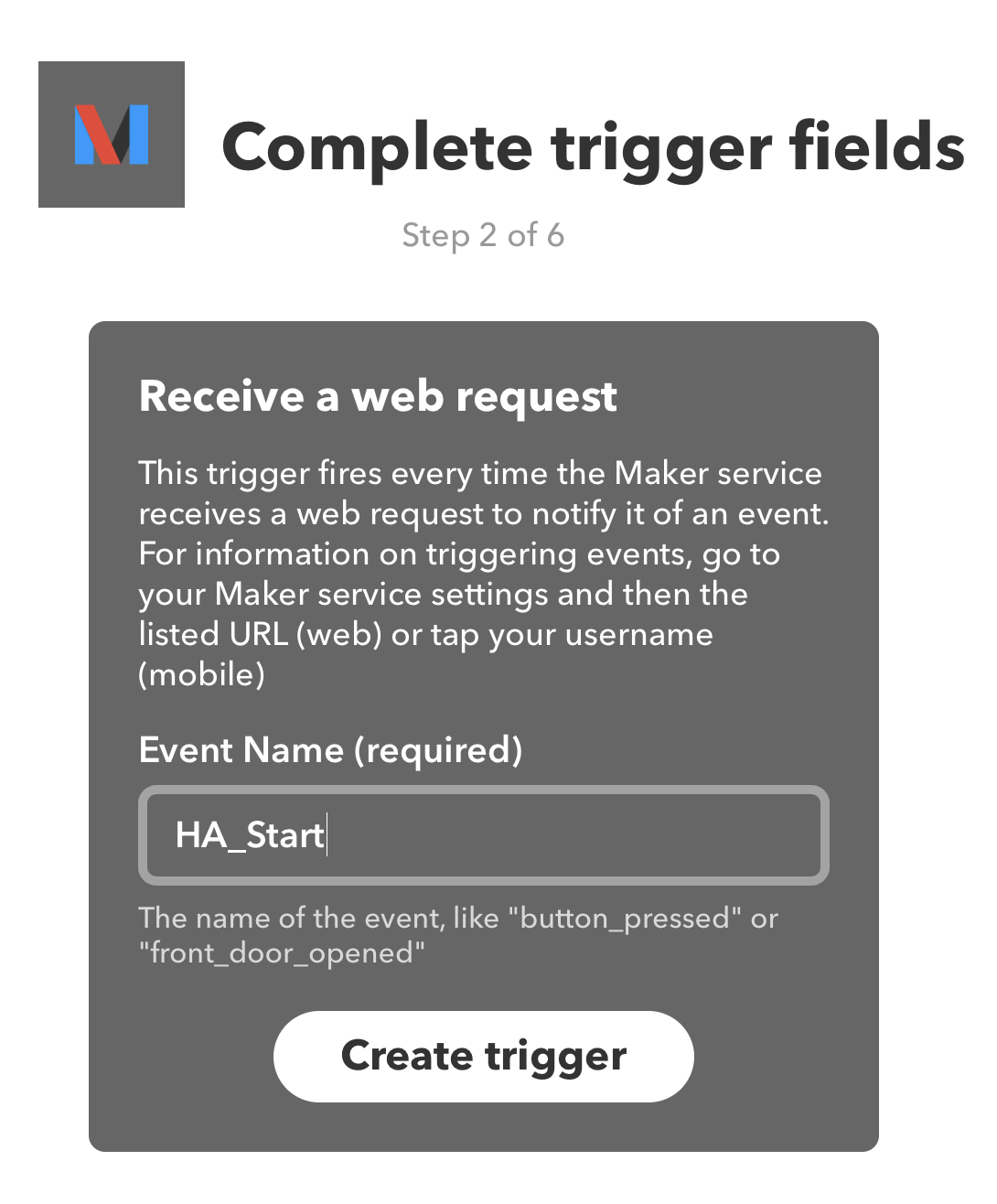
之后在 HomeAssistant 里面就可以通过这个名字触发这条 IFTTT 了。在此之前,我们先把下面的 that 步骤完成,为了直观地看到测试效果,我们选择 Notifications - Send a notification from IFTTT app
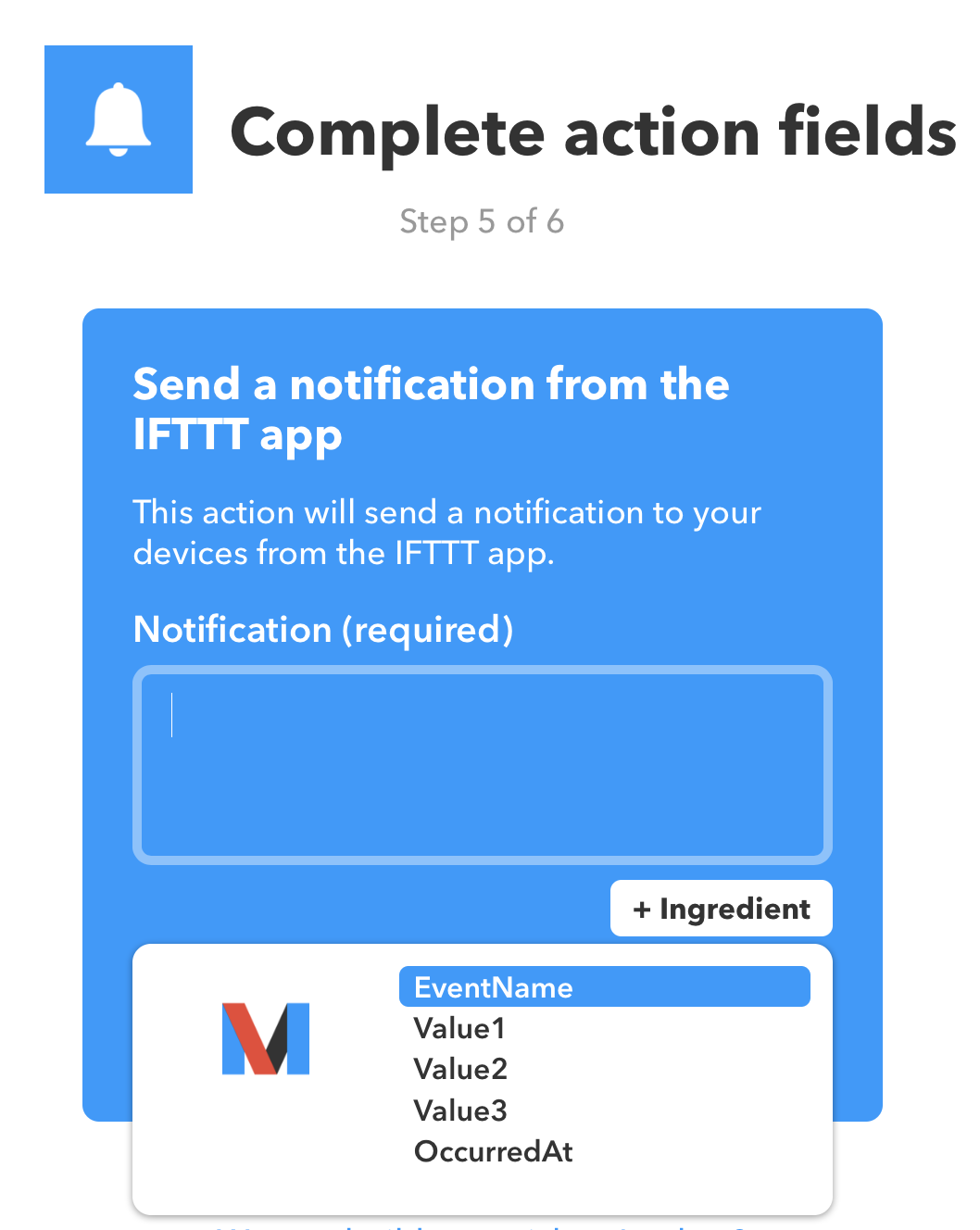
这里有很多 Ingredient 占位符, EventName 就是之前我们给事件声明的名字,Value1,Value2,Value3 我们可以在 HA 里面自己传过去,OccurredAt 就是发生的时间。
创建完成这条 Applet 之后,我们就可以开始用 HA 来触发了。触发的方式就太多了。
1.最简单的,在我们的管理界面:
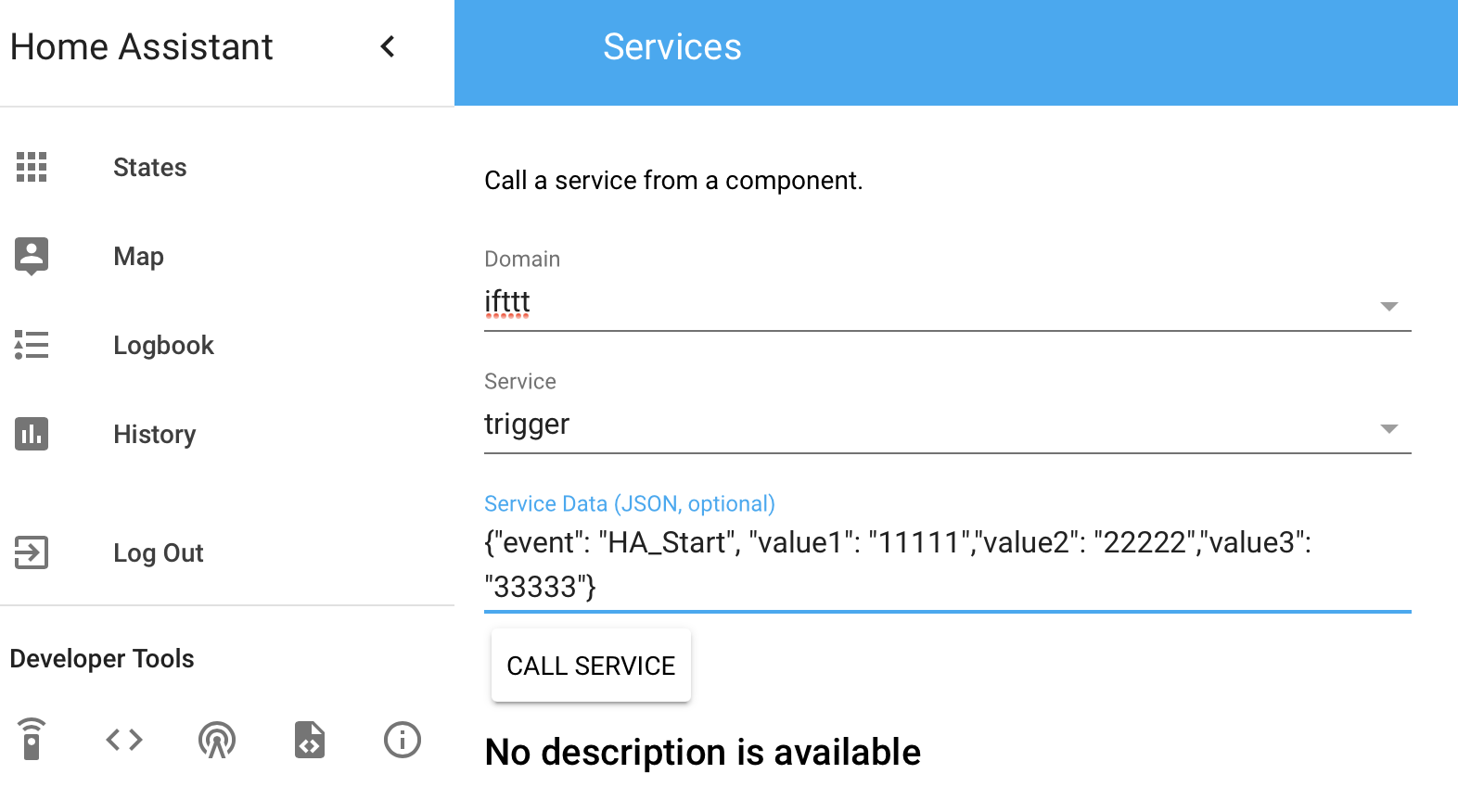
event 字段后面就跟我们之前填写的事件的名称,后面的 Value1,2,3 对应之前 IFTTT 里的参数。然后点击 CALL SERVICE ,不出意外就可以在几秒钟之后看到 IFTTT 给你推送了一条消息。
2.其次我们还可以在 automation 里的 action 中触发
action:
- service: ifttt.trigger
data: {"event":"HA_Start", "value1":"Home Assistant 已启动"}
3.RESTful API 这真的是个强大功能。这意味着我们可以像调用普通 API 一样调用 HomeAssistant 的所有服务。由于太过强大,我另起一节介绍。
4. RESTful API 文档
和普通的 RESTful API 一样, HA 的 RESTful API 也是返回的 JSON 格式,另外,如果你配置了HTTP 这个服务并设置了密码(这个密码就是你登录控制面板的密码,推荐这么做),那么你只需要在调用 API 的时候传入密码参数即可。
具体 API 请大家看文档,我仅介绍比较常用的以做示范。
GET /api/services -- 获取当前可用的所有服务
[
{
"domain": "ifttt",
"services": {
"trigger": {
"description": "",
"fields": {}
}
}
},
{
"domain": "switch",
"services": {
"toggle": {
"description": "Toggles a switch state",
"fields": {
"entity_id": {
"description": "Name(s) of entities to toggle",
"example": "switch.living_room"
}
}
},
"turn_off": {
"description": "Turn a switch off",
"fields": {
"entity_id": {
"description": "Name(s) of entities to turn off",
"example": "switch.living_room"
}
}
},
"turn_on": {
"description": "Turn a switch on",
"fields": {
"entity_id": {
"description": "Name(s) of entities to turn on",
"example": "switch.living_room"
}
}
}
}
},
{
"domain": "light",
"services": {
"toggle": {
"description": "Toggles a light",
"fields": {
"entity_id": {
"description": "Name(s) of entities to toggle",
"example": "light.kitchen"
},
"transition": {
"description": "Duration in seconds it takes to get to next state",
"example": 60
}
}
},
"turn_off": {
"description": "Turn a light off",
"fields": {
"entity_id": {
"description": "Name(s) of entities to turn off",
"example": "light.kitchen"
},
"flash": {
"description": "If the light should flash",
"values": [
"short",
"long"
]
},
"transition": {
"description": "Duration in seconds it takes to get to next state",
"example": 60
}
}
},
"turn_on": {
"description": "Turn a light on",
"fields": {
"brightness": {
"description": "Number between 0..255 indicating brightness",
"example": 120
},
"color_name": {
"description": "A human readable color name",
"example": "red"
},
"color_temp": {
"description": "Color temperature for the light in mireds (154-500)",
"example": "250"
},
"effect": {
"description": "Light effect",
"values": [
"colorloop",
"random"
]
},
"entity_id": {
"description": "Name(s) of entities to turn on",
"example": "light.kitchen"
},
"flash": {
"description": "If the light should flash",
"values": [
"short",
"long"
]
},
"profile": {
"description": "Name of a light profile to use",
"example": "relax"
},
"rgb_color": {
"description": "Color for the light in RGB-format",
"example": "[255, 100, 100]"
},
"transition": {
"description": "Duration in seconds it takes to get to next state",
"example": 60
},
"white_value": {
"description": "Number between 0..255 indicating level of white",
"example": "250"
},
"xy_color": {
"description": "Color for the light in XY-format",
"example": "[0.52, 0.43]"
}
}
}
}
}
]
你实际的 JSON 内容一定比我上面的要多,因为我删了一些不常用,留下精华做示范。可以看到最外面是个数组,每个元素都是一项服务,我留下了 ifttt,switch,light,之所以会出现三个服务,就是因为你在 Configuration.yaml 里面添加了这三个服务。根据上面返回的信息,我们可以写出调用 IFTTT 服务的 API 如下:
API: http://YOUR_IP_ADDRESS:8123/api/services/ifttt/trigger?api_password=YOUR_PASSWORD (YOUR_IP_ADDRESS 可以是局域网IP,也可以是域名)
Method: POST
Content-Type: application/json
Params: {"event": "homeassistant_start", "value1": "来自的 RESTful API 的推送"}
这里推荐一个 Mac 上我常用的测试 API 的工具 —— Cocoa Rest Client.
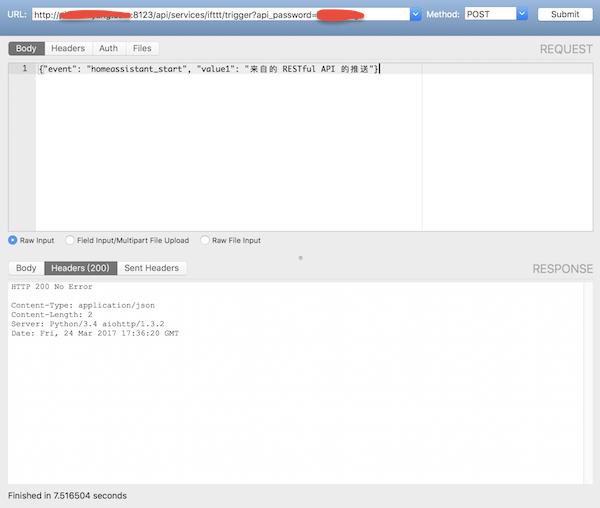
显示 HTTP 200 No Error 说明没有问题,接下来的几秒内你就会收到一条推送了。现在,你是不是和我一样觉得神奇之余还有一丝成就感。
更进一步,你看到我上面还有 'light' 和 'switch' 这两个服务,这些是因为我配置了硬件相关的服务后出现的,这也就意味着你可以用 API 来控制你的电视,空调,灯泡灯一切电器。
例如通过 API 开启空气净化器:
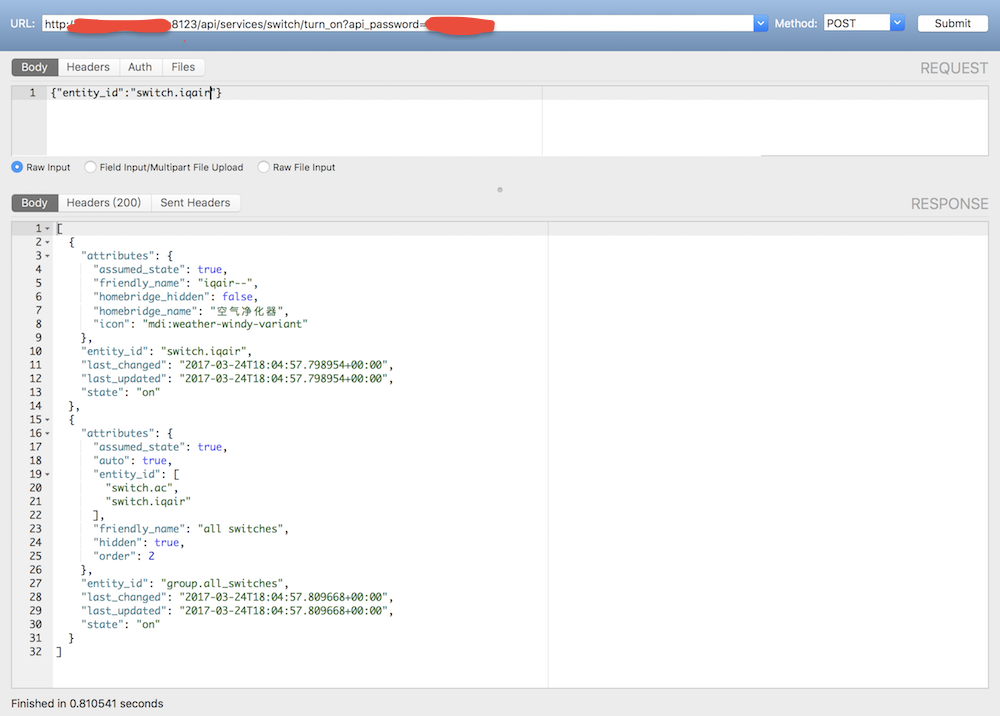
通过 API 开启 Yeelight智能灯泡并切换到指定颜色和亮度:
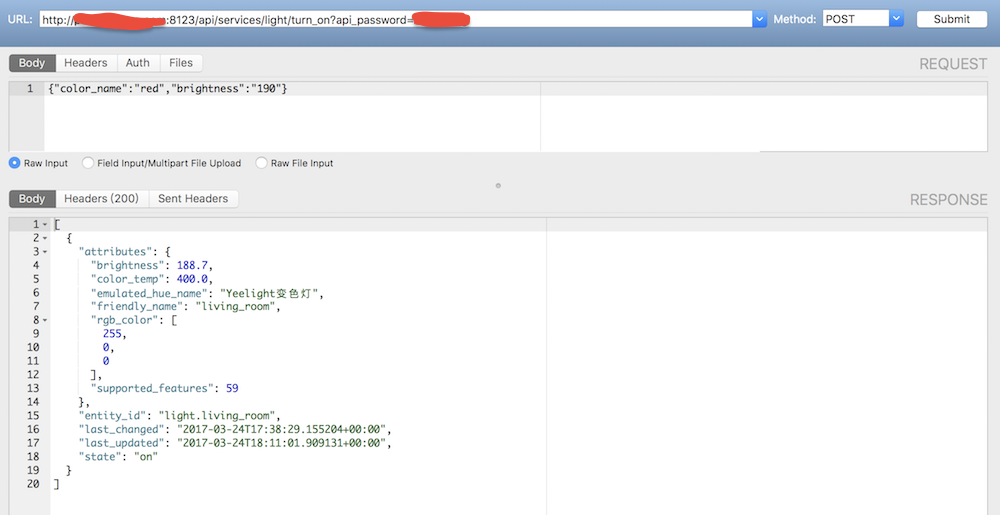
比如我还写了一个 Shell 脚本每天早晨8点自动运行,通过 API 获取 World Air Quality Index 的空气质量数据,如果 PM2.5大于50就通过 API 让床头灯颜色显示红色,否则显示绿色,这样我早上醒来一看床头灯的颜色就知道今天要不要带口罩了。
#!/bin/bash
# get AQI
MY_VAR="$(curl https://api.waqi.info/feed/shanghai/?token=xxxxxxxx | jq "{aqi: .data.aqi, pm25: .data.iaqi.pm25.v, pm10: .data.iaqi.pm10.v}")"
echo $MY_VAR
pm25="$(echo $MY_VAR | jq ".pm25")"
if [[ $pm25 -gt 50 ]]; then
echo "PM2.5 大于50"
curl -X POST -H 'x-ha-access: xxxxx' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{"color_name":"red","brightness":"190"}' \
http://IP_ADDRESS:8123/api/services/light/turn_on?api_password=PASSWORD \
fi
想到平时一直接触的 API 竟然可以用来控制你的电器,是不是又一次感觉不可思议。这一切,都归功于 HomeAssistant 这个成熟的开源社区,再次表达敬佩和感谢之情。
其实当 IFTTT 的 Maker Webhooks 作为 that 部分的时候,也可以充当调用 API 的发起方(Make a web request)。比如我的一条 IFTTT 是:当我到家的的时候自动开启所有电器。这里面 Maker Webhooks 作为了 that 部分就可以发起一个 HTTP Request 了。
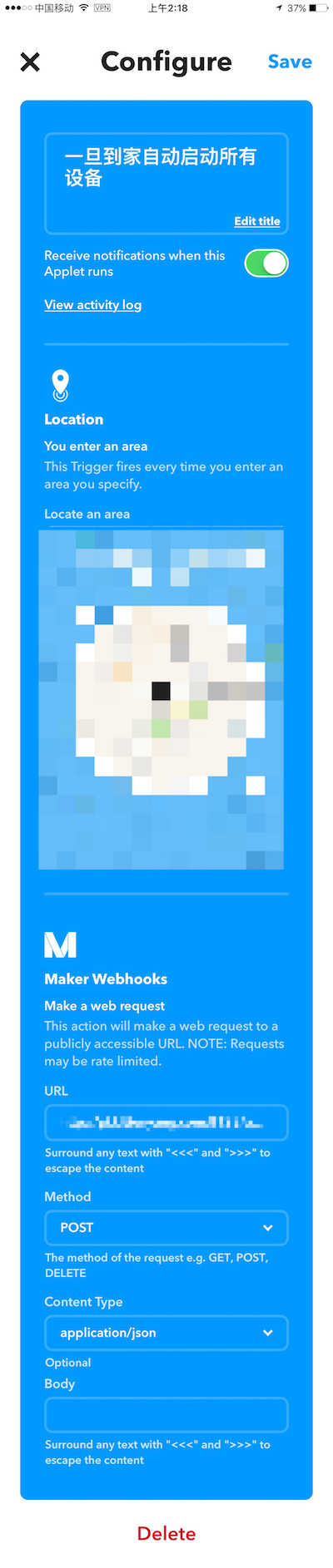
至此,通过 API 实现了 IFTTT 和 HA 全部打通,两者既可以作为主动发起方,也可以作为被动执行方,简言之,你可以让 HA 触发一条 IFTTT,IFTTT 再触发硬件,也可以 IFTTT 触发 HA 的 automation,automation 再触发其他操作..... 总之已经可以结合出无数多的可能性,限制你的只有你的想象力。
好啦,下一篇文章,我们要开始接入硬件了,要知道我前面铺垫了这么久,最终要实现的功能还是用 Amazon Echo 和 Siri 控制所有家电啊。
